Plastic Injection Molding Specialist
- Your Plastic Injection Molding Expert since 2002
- More than 200 injection molding machines from 25 to 850 tons
- Top quality secondary processing and assembly
Plastic Materials Available
Formlabs Clear Resin
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is made up of acrylonitrile A, butadiene B, and styrene S copolymers. Each monomer has its own set of properties. ABS is a type of amorphous plastic. It is defined by its low-temperature resistance, impact resistance, appearance qualities, low creep, good size stability, and ease of processing. In addition, the surface hardness is great, and the chemical resistance is excellent. ABS engineering plastics offer a wide range of uses because the proportions of the above three components can be altered to vary the qualities of ABS. The synthesized ABS can be divided into four categories: medium impact type, high impact type, ultra-high impact type, and heat resistant type.
ABS plastic has a higher molding temperature, so the mold temperature should be set at 30-70°C. The fixed mold-half temperature is about 5°C higher than the moving mold-half temperature when fabricating large parts. The product look quality is affected by the mold temperature, a lower temperature will result in a worse quality appearance.
Melt adhesive should be processed at a temperature of 190-235°C. ABS has a medium melt viscosity and must be generated at a high injection pressure (500-1000bar). Injection of ABS plastic produces superior results at medium and high speeds.
ABS plastic is highly hygroscopic and sensitive to humidity, so it must be dried for at least 2 hours at 90°C before molding. Moisture levels should be kept below 0.03 percent.
PA (Nylon-Polyamide)
Nylon is a polyamide with several variants, the most popular of which are PA6 and PA66, followed by PA11, PA12, PA610, PA612, PA46, and so on.
Nylon has good mechanical strength, a low friction ratio, and self-lubrication, it also has oil resistance, as well as, weak acid, alkali, and general solvent resistance. In addition to good electrical insulation. It is non-toxic and odorless . It has a high water absorption rate, but fiber reinforcing can lower the resin’s water absorption and allow it to work in high-temperature and high-humidity environments.
Nylon is a crystalline plastic with a high melting point, a narrow melting temperature range, and low heat resistance. The absorption of moisture in the molding process results in a big decline in viscosity, and when mixed with bubble products on the surface of silver wire, the mechanical strength of the products is reduced, therefore the material must be dried before treatment, it can be dried at 80-110°C for 6 hours. However, PA plastic that dries at temperatures exceeding 90°C is prone to discolouration.
PA has good fluidity, therefore it can be heated and used with a self-locking nozzle. Simultaneously, because of the solution’s rapid condensation rate, product shortages caused by materials clogging nozzles, runners, and gates should be avoided. The mold overflow edge value is 0.03. The melt viscosity is sensitive to changes in temperature and shear force, but it is more susceptible to temperature. When processing PA we should start by lowering the barrel temperature to reduce its melt viscosity. It has a wide range of forming shrinkage, excellent direction, and is susceptible to shrinkage, deformation, and other effects.
PC (Polycarbonate)
Polycarbonate is a type of engineering plastic that is extensively used and belongs to the non-crystalline plastics category. It has great impact resistance, high tensile strength, outstanding bending strength, low shrinkage, low thermal creep, high dimensional precision, good heat resistance, and low-temperature resistance, among other good mechanical properties. In addition to this, polycarbonate has advantages such as high transmittance, high refractive index, high impact resistance, and dimensional stability. Film projector lenses, photocopier lenses, infrared auto-focusing projector lenses, and laser beam printer lenses are all applications of optical lenses made out of optical grade polycarbonic acid, as well as, cameras, microscopes, telescopes, prisms, mirrors, optical testing devices and household appliances.
It works in temperatures ranging from -60 to 120 degrees Celsius. Low fatigue strength, low solvent resistance, and poor wear resistance, as well as its proneness to brittleness are some of the limitations of the material. Polycarbonate should be dried at a temperature of 120 degrees Celsius for at least 4 hours. The mold temperature is normally between 80 and 120 degrees Celsius. The temperature of the injection is between 280 and 320 degrees Celsius. In production, a slow injection speed and a high injection molding pressure should be used. When the mold temperature is low, shrinkage and elongation are minimal, impact strength is poor, and bending, compression, and tensile strength are all low. When the mold temperature exceeds 120 degrees Celsius, the plastic parts cool slowly.
PC/ABS
It’s made from a synthesization of PC and ABS. It. PC is polycarbonate, and ABS is the copolymer of acrylonitrile (A), butadiene (B), and phenylephrine (S). PC/ABS combines the benefits of both PC and ABS in one package. For example, ABS is simple to produce, whereas PC has great mechanical qualities and thermal stability. On the one hand, it can improve ABS’s heat resistance, impact resistance, and tensile strength; on the other hand, it can lower polycarbonate’s cost and melt viscosity, improve processability, and minimize the susceptibility of internal stress and impact strength to product thickness. Similarly, the thermal stability of PC/ABS materials is affected by the ratio in which they are manufactured.
In addition to this, PC/ABS has outstanding flow properties. It has a shrinkage of around 0.5 percent. Before processing, PC/ABS must be dried. the drying conditions should be 90mm 110°C for 2 hours and the humidity should be less than 0.04 percent; the melting temperature should be around 230m 300°C; the mold temperature must be within 50m 100°C; the injection pressure is dependent on the plastic parts, and the injection speed is not required, but it is preferable to be as high as possible.
On the other hand, some of the applications of this material include: computers, photocopiers, and electronic and electrical components, as well as, automobile decorating pieces, lamp housing, and heat-resistant electrical shells. Flame retardant, glass fiber reinforced, electroplating, UV resistance, and other innovative PC/ABS alloy variations are available.
PE (Polyethylene)
Polyethylene is a thermoplastic resin that is manufactured by polymerizing ethylene, it comes in a variety of forms such as LDPE, MDPE, HDPE, LLDPE. At room temperature, it is indissoluble in general solvent and has minimal water absorption and high electrical insulation. It is also resistant to low temperatures (the lowest temperature it may reach is 70°C), has strong chemical resistance, and can withstand corrosion by most acids and alkalis (not resistant to oxidation). Additionally, it has the feel of wax and is nontoxic and inodorous.
On the other hand, the temperatures for injection molding of this material must be set as follows: mold temperature 10-70℃, material pipe temperature 150-210℃,injection nozzle 140-190℃, front section 140-200℃, middle section 130-180℃,back pressure 5~10KG, injection pressure 360-500KG / cm² and screw speed 210-220RPM.
PEEK (Poly ether ether ketone)
PEEK is a type of special engineering plastic that consists of an aryl group, ketone bond, and ether bond in a macromolecular polymer. It is commonly used in construction machinery and aerospace items due to its many qualities, including high temperature resistance, great flame retardancy, and excellent chemical stability. PEEK plastic has a positive high-temperature resistance of 260°C and a hot deformation temperature of 160°C. The thermal deformation temperature can be enhanced to 280-300°C by adding 30% glass fiber. Similarly, melt fluidity, thermal stability, corrosion resistance, high strength, and easy formability are all features of PEEK polymers, as well as, great hydrolysis resistance, and high temperature resistance, it can withstand acids and alkali substances and practically any chemical reagent with the exception of concentrated sulfuric acid. Likewise, PEEK material has outstanding electrochemical properties.
On the other hand, because of its remarkable high-temperature resistance, heat resistance, strong height, and machinability, PEEK polymers are commonly used in the aerospace and automobile industry,chemical industry, and in electrical equipment among other areas.
PMMA (Acrylic)
PMMA acrylic plastics have a density of 1.19-1.22g/10cm³ and are stiff and transparent. The most notable property of PMMA acrylic plastic is its great transparency, with a light transmittance of 92 percent, the highest among polymers, and UV transmission of up to 75 percent. Some of the special qualities the material possesses include: good chemical stability, resistance to salts, oils and diluted inorganic acids, (although it is not resistant to concentrated inorganic salts, hot alkali, ketones, chlorinated hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, etc), good resistance to ozone, outstanding arc resistance, good insulating and dielectric properties, as well as, atmospheric aging resistance.
Likewise, it has many good mechanical properties: it has stronger tensile, compressive, and bending strengths than PE, PVC, and PS, but it has poor impact toughness, making it a hard and brittle material. PMMA has a low heat resistance, with a melting temperature of 160-200°C, a thermal decomposition temperature of 270°C and a glass transition temperature of 104°C.
PMMA acrylic plastics are widely used in the manufacture of optical glasses such as lenses, prisms, reflectors, and camera lenses. It can also produce lamps, lighting equipment, instrument dials, as well as, aircraft cabin glass, bulletproof glass, optical fiber, and other materials.
POM (Polyoxymethylene-Acetal/Delrin)
POM, also known as paraformaldehyde, is an engineering thermoplastic that has good creep properties, geometric stability, and impact resistance even at low temperatures while still retaining its ductile and elastic properties. POM has a low friction coefficient and good geometric stability, making it ideal for the manufacture of gears and bearings. It has high hardness, high steel, and high wear resistance as its main mechanical properties, and because POM has high-temperature resistance, it can also be used in pipeline equipment (pipe valves, pump shells), lawn equipment, and other applications. In addition to this, POM has a high elastic modulus, hardness, and stiffness due to its extremely crystalline nature
Furthermore, its homopolymerization thermal deformation temperature is 136°C, and the copolymerization thermal deformation temperature is 110°C. Co-formaldehyde, on the other hand, has a greater continuous use temperature due to its distinct molecular configurations. POM’s long-term use temperature is typically about 100°C and its long-term heat resistance temperature is 85-105°C. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40 to 100°C for an extended period of time. It can also resist repeated shocks for a long time with little loss in strength. Temperature and temperature variations have little effect on the strength.
Furthermore, 190-220°C is the melting point that should be met during injection molding. Otherwise, the substance decomposes when the melting temperature is too high. POM should be injected at a medium pressure, at a medium speed, with a moderate material temperature and a high mold temperature. The holding pressure should also be increased during the injection molding process to reduce pressure drop. The screw speed should be appropriate, not excessively high, and residue should be minimized; the appropriate mold temperature is (80mm 100°C).
PP (Polypropylene)
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer resulting from the polymerization of propylene. It is partially crystalline and nonpolar. It has the best heat resistance of all the general-purpose polymers. Products constructed of PP can be cooked in 100°C water with a distortion temperature of 80-110°C. PP is resistant to stress cracking and has a long warping fatigue life. Additionally, PP is the lightest of the regularly used polymers, with a density of only 0.90-0.91g/cm3. Some other advantages of the material include: toughness, high chemical corrosion resistance and lightness. In contrast, it also has poor weather resistance, low dimensional precision, insufficient rigidity and it is prone to brittleness, aging, post-shrinkage and warpage after demoulding.
During the injection molding process the melting temperature must be set to 220-250℃, no more than 250℃, drying the material prior to it is not necessary if it is properly stored. In addition to this, a mold temperature of 40℃ is encouraged. This temperature determines the degree of crystallization. Likewise, the injection pressure can reach 1800 bar and using high-speed injection molding can minimize internal pressure.
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide)
Polyphenylene sulfide is well-known for its thermal stability ,it’s commonly utilized in special technical plastics. High stiffness, high surface hardness, exceptional creep resistance, and fatigue resistance are some of the mechanical qualities of PPS plastic. It has other outstanding qualities such as high temperature resistance, flame retardancy, corrosion resistance, weather resistance, dimensional stability, and electrical properties.
At present there is no solvent that can dissolve PPS below 200℃, and it is highly resistant to inorganic acids, bases, and salts. Moreover, the thermal deformation of PPS is over 260 ℃, one of the highest temperatures of thermoplastic engineering polymers, its long-term use temperature is 220-240°C and its short-term temperature is 260°C. It can also be manufactured into high-strength materials with good electrical conductivity after modification. It has high volume resistivity, surface resistivity, breakdown voltage, low dielectric constant, and dielectric loss angle tangent in high temperature, high humidity, and high frequency environments, making it an effective insulating material.
On the other hand for the injection molding process, the material is dried for 3 hours at 130-150°C, the mold temperature is 120-180℃, the barrel temperature is 280-330℃, the 40%GF+PPS is 300mm and the injection should be performed at medium speed and 50-130V MPA.
PS (Polystyrene)
Polystyrene is a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer made from the monomer known as styrene, it usually has the form of a glossy, transparent bead or granular solid. Some examples of PS include: expandable polystyrene (EPS), high impact polystyrene (HIPS), and metallocene polystyrene (SPS). Polystyrene can survive the effects of some organic acids, bases, mineral oils, salts and lower alcohols;chlorinated hydrocarbons,aromatic hydrocarbons, aliphatic ketones, and esters are all soluble in it. Moreover, its electrical performance is outstanding; it is unaffected by changes in temperature and humidity. It also has a low water absorption rate and can retain its mechanical characteristics even with high humidity. Only acrylic resins have better optical characteristics.
The product’s melting temperature is 150-180°C, its thermal decomposition temperature is 300°C, its thermal deformation temperature is 70-100°C, and its long-term service temperature is 60-80°C. Its main disadvantages relating to mechanical properties include: low impact strength, brittleness, poor heat resistance, that it is unable to withstand boiling water, must be used at low temperatures and that it is flammable.
Furthermore, during the injection molding process this material can be used without drying, nevertheless it can be pre-died at an oven for 1- 2 hours at 55-70℃ in order to improve the quality, the mold temperature should be set at 60℃ 80℃ and the injection temperature at 170℃-220 ℃, barrel temperature should be about 200℃. Molded products can be treated at 70°C for 2 hours in an infrared lamp or blast oven to remove internal stress.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is one of the most widely produced synthetic polymers of plastic. Some of the key characteristics of PVC are its excellent chemical resistance, it can withstand concentrated hydrochloric acid, and also nitric acid, sodium hydroxide, and sulfuric acid to certain percentages, it has good mechanical strength and good electrical insulation.
PVC resin’s softening point is close to its breakdown temperature. The two most critical process indices for ensuring proper PVC resin processing are decomposition temperature and thermal stability. Unless alkaline stabilizers are applied, PVC polymers will degrade for a long period at 100°C. It will swiftly degrade if the temperature rises above 180°C.
PVC is a versatile material with numerous applications such as window frames, drainage pipe, water service pipe, medical devices, blood storage bags, cable and wire insulation, resilient flooring, roofing membranes, stationary, automotive interiors and seat coverings, fashion and footwear, packaging, and so on.
Finally, during injection molding the drying temperature should be set to 80℃ for 2h,the mold temperature to 30-60℃, the material pipe temperature to 160-190℃, and the forming shrinkage should be about 0.1-0.5%. The injection pressure can reach 1500bar and the holding pressure can reach 1000bar. To avoid material degradation, appropriate injection speed is required.
Types of Finishing
Formlabs Clear Resin
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
SPI A (Mirror)
Including SPI A0, A1, A2, A3, the engineering mold part is smoothed and polished with a diamond buff to produce pieces with a mirror-like surface.
SPI B (Sandpaper)
Including SPI B0, B1, B2, B3. We give a fine surface, smooth finish to engineering molds using fine-grit sandpaper.
SPI C (Stone)
It includes SPI C1, C2, and C3. All machining marks are removed from the part by smoothing it with fine stone powder.
SPI D (Sandblasting)
First the mold is polished with fine stone, then it goes through a process called sandblasting.
Texturing (Grain)
A textured finish is a rough surface created by spraying and splattering big drops of coating onto previously placed coating. Textured coatings are the coatings that are used to provide the look of the textured finish.
EDM (EDM Sparking)
A surface finish achieved by EDM differs from one created by conventional material removal methods. The texture is random rather than directed, which is advantageous in many applications. Furthermore, by doing repeated skimming passes, the EDM finish quality can be nearly mirror-like.
Automated Injection Molding Production
In IMP we can help you improve the quality of your products and lower the costs with our automated injection molding services. As an ISO 9001:2015-certified manufacturer we optimize the supply of high-quality, low-cost plastic components by producing plastic parts on high-output automated injection molding process lines. Additionally, our staff of highly qualified technicians and engineers overviews other manufacturing processes including: product and mold design, prototyping, mold manufacturing, secondary processing, assembly and final delivery.

Injection Molding Streamlined Production
In IMP we use new robotics and automation technology in injection molding process lines to decrease costs and shorten lead times. Once the mold has been developed and the processes have been perfected, just one operator is required for control and management. Production can continue after hours if necessary due to the precision and quality of our machinery. Other advantages include: reduced waste, enhanced product quality, increased repeatability, among others.

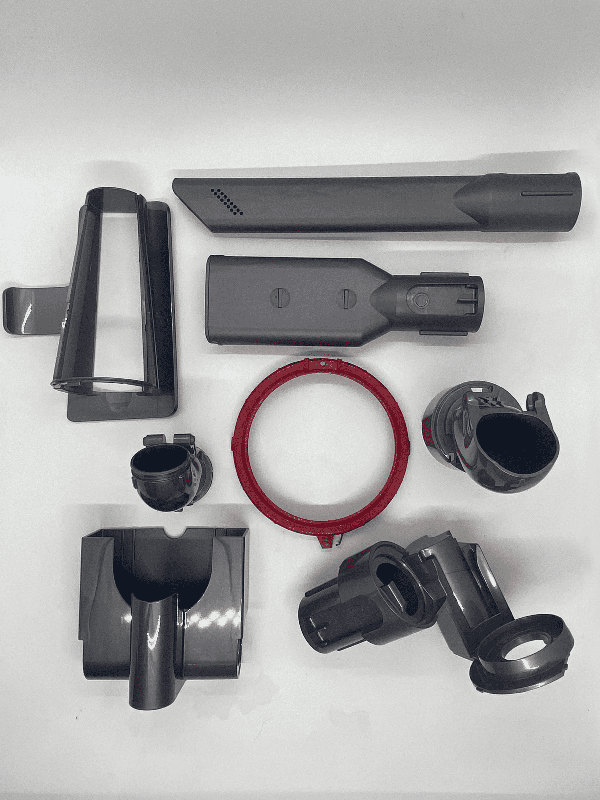
In IMP we offer you our excellent plastic injection overmolding services, we specialize in integrating layers of elastomeric materials to plastic parts to produce adaptable, high-performance end products.
This process enhances the utility, durability and appearance of stiff structural components that are bonded with a flexible material. Overmolding often reduces the time and cost required to manufacture a part.

Advantages of Overmolding
- Increases overall strength of the part
- Improved resistance against water and toxins
- Better electrical resistance
- Enhanced usability
- Reduced noise and vibration
- Better handling
Applications of Overmolding
Overmolding can produce a wide range of items including cookware, hardware tools, surgical devices, cables, electrical circuits, custom metal components, car trims, knobs, among others.

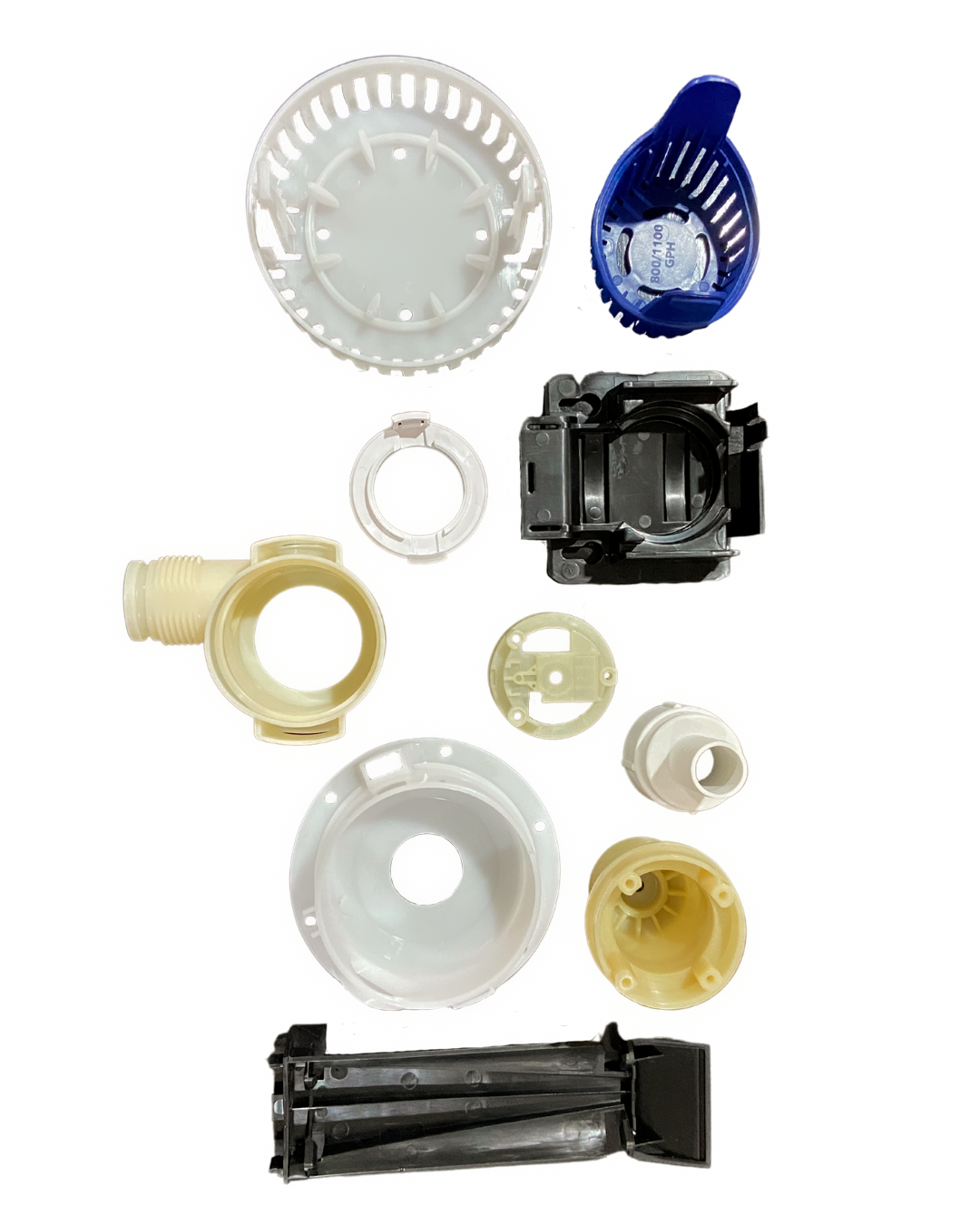
Small Part Injection Molding Advantages
The part with the smallest tolerance produced by IMP so far had a tolerance of 0.05 mm. Some advantages of Small Part Injection Molding include:
- Small batch to large scale production
- High repeat tolerance
- Precision manufacturing
- Variety of colors (custom colors available)
- Material flexibility
- Mold transfer capability
- Minimal scrap
- Lower part price
- Minimal finishing requirements
- Tooling
Small Part Injection Molding
IMP is an ISO 9001:2015-certified company with over 20 years of small component injection molding experience. We provide our customized service for the more specialized and challenging products. We can meet the most stringent specifications and the highest tolerances.
Insert Injection Molding
IMP has been producing high-quality insert molds for over 20 years thanks to our extensive experience and competent team. In IMP we design and manufacture molds in accordance with European and American standards, we make sure that molds perfectly accommodate inserts and that the inserts are thoroughly developed and made to perfectly fit the plastic parts. Furthermore, at IMP we use hardened steel for insert injection molds and provide steel and heat-treat certification for insert injection molds to ensure that we provide quality molds with an extended life.
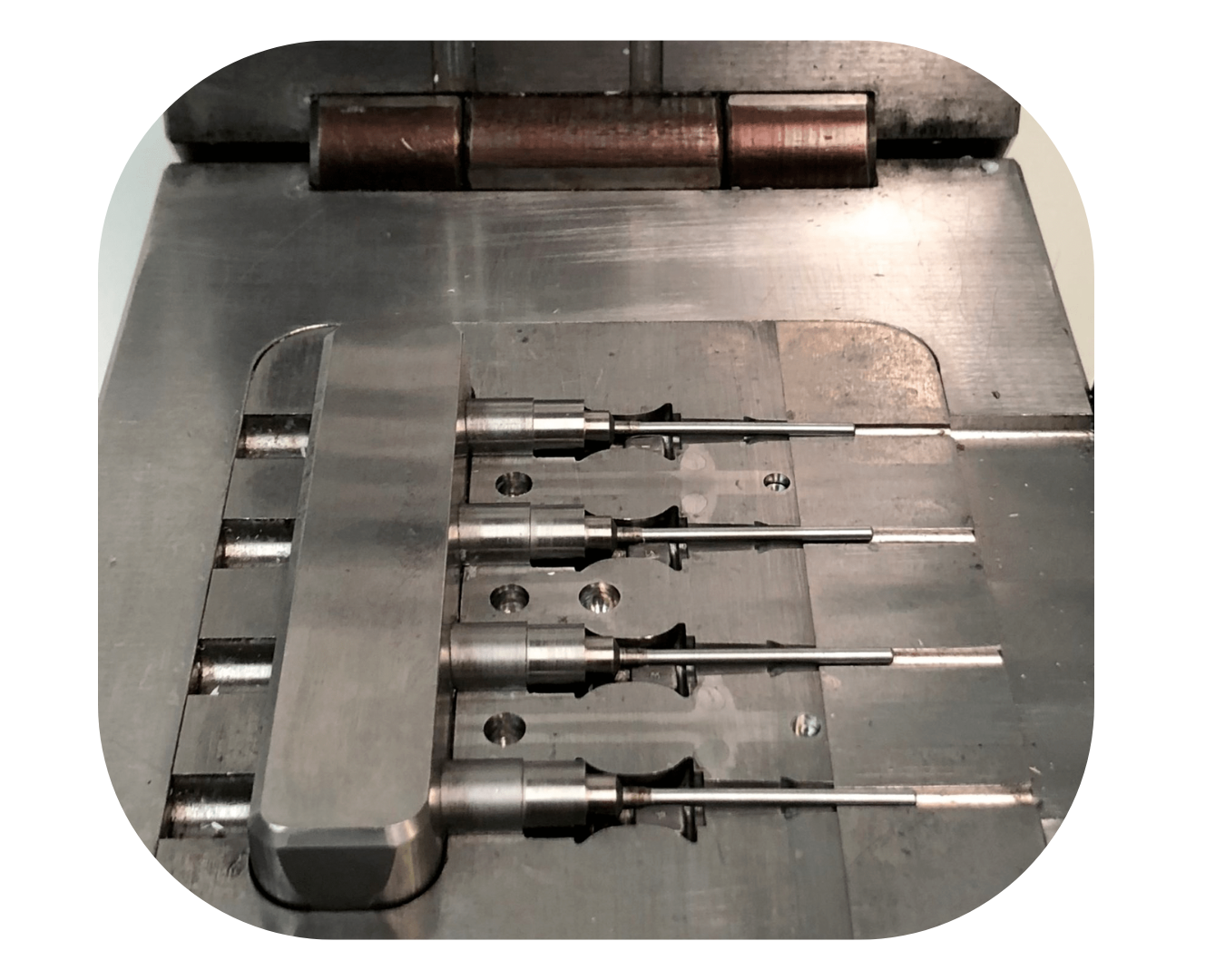
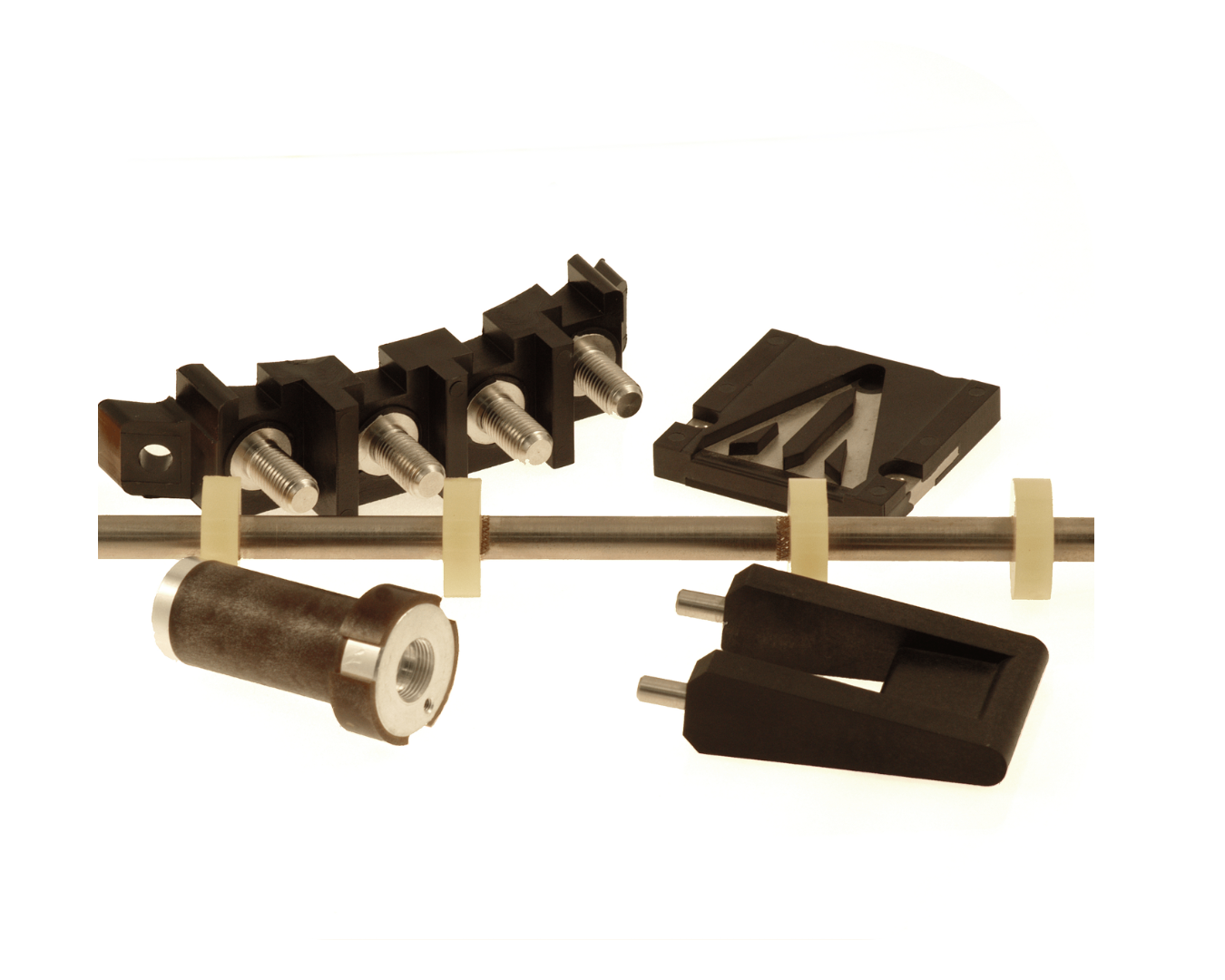
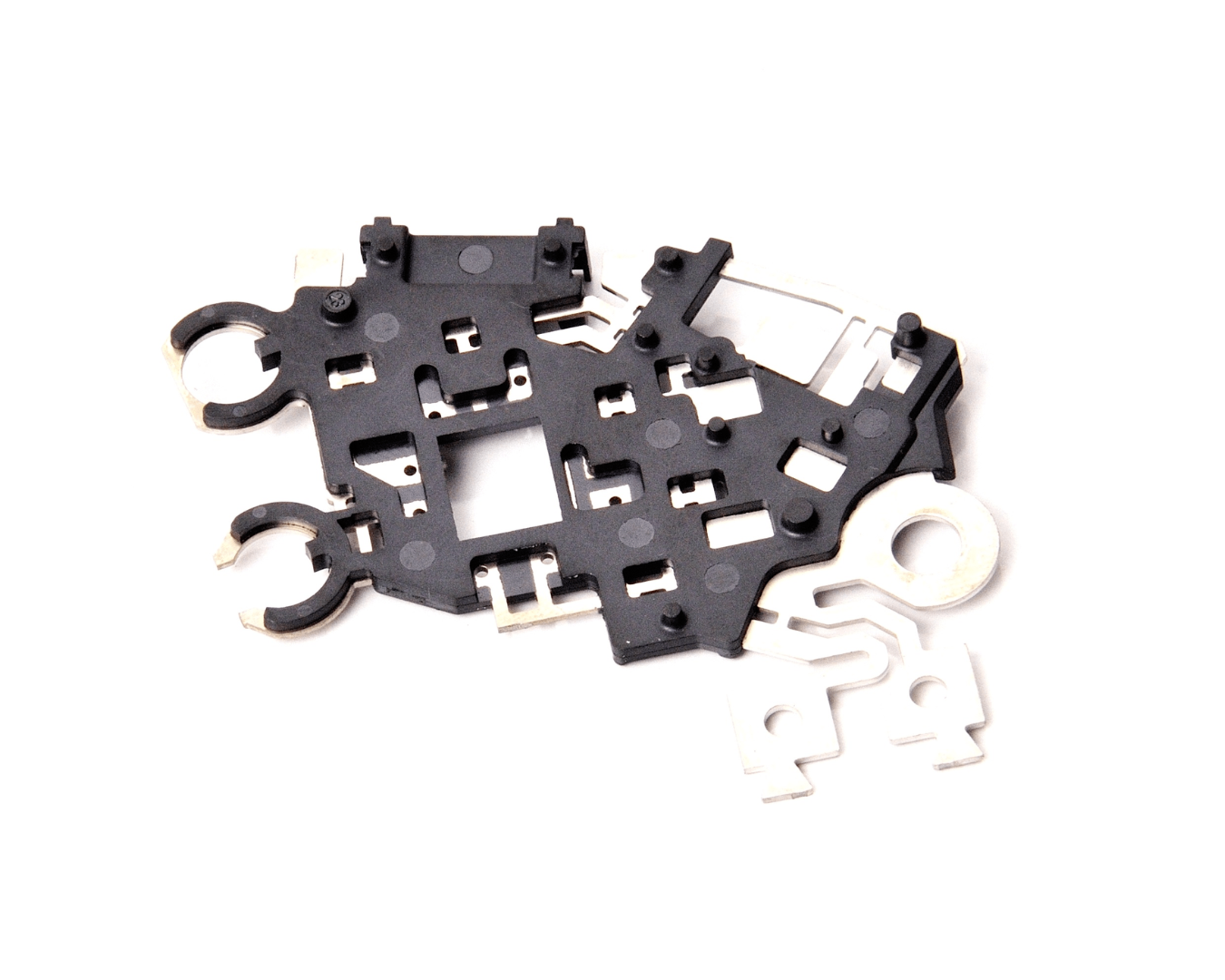
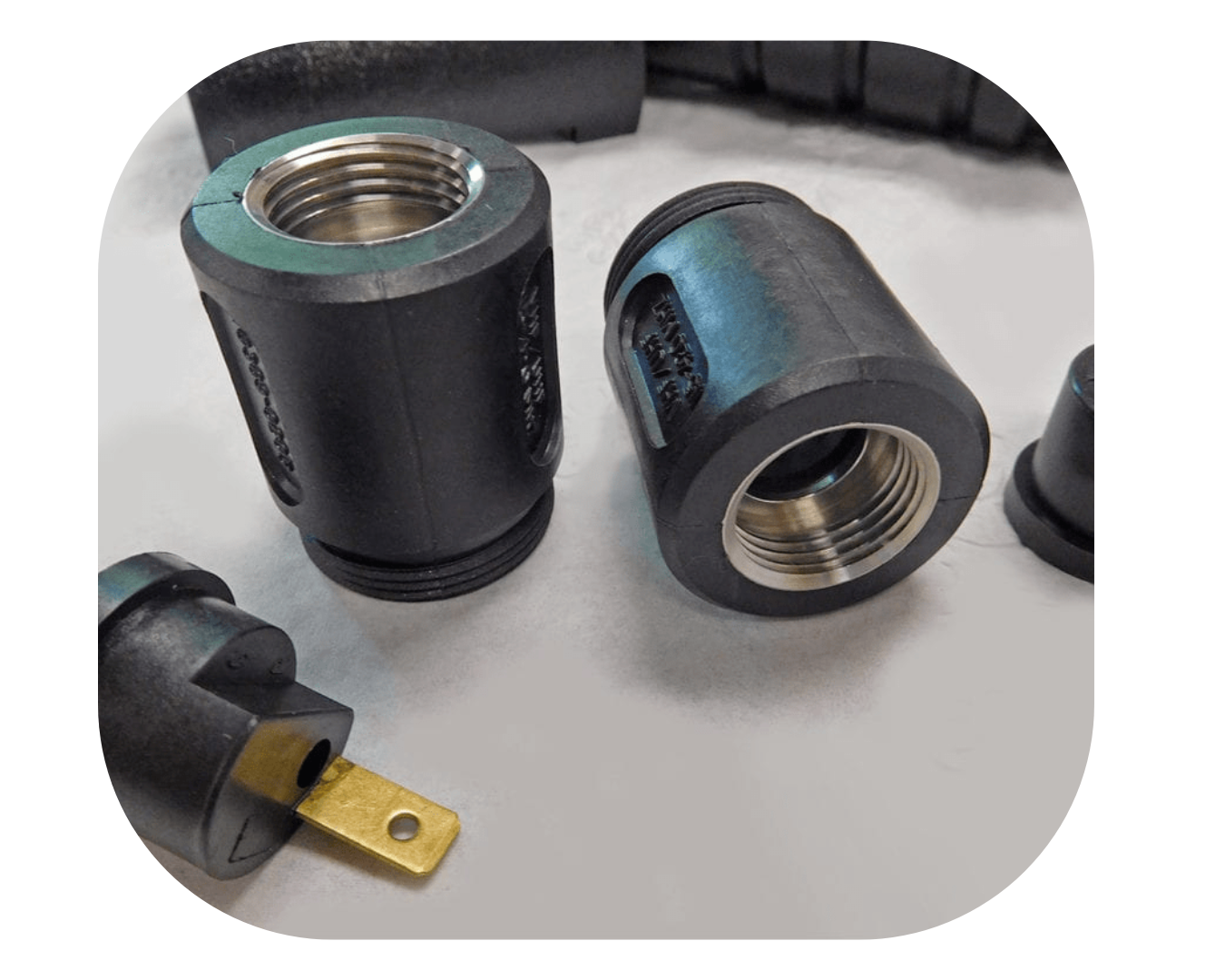




Let’s Work Together
We will be honored to hear about your project and to help you execute it.
